
Build a strong foundation in Basic Mathematics for Class 1-3 with concepts like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, place value, and Fun games
Mathematics is a crucial subject that lays the foundation for logical reasoning, problem-solving, and analytical thinking. For students in classes 1 to 3, mastering the basic concepts of mathematics is essential for their academic growth and future success. This article delves into the fundamental concepts of addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, understanding place value, and simple fractions. Additionally, we’ll explore engaging math games and puzzles that make learning fun and effective.
Understanding the Basics Mathematics

Mathematics in the early grades is all about building a strong foundation. The concepts learned in classes 1 to 3 are the building blocks for more complex mathematical ideas in higher grades. It’s essential to ensure that students grasp these fundamental concepts thoroughly.
Addition: The First Step in Arithmetic
Addition is the most basic operation in Basic Mathematics. It involves combining two or more numbers to find their total. At the class 1 level, students start with single-digit addition and gradually move to double-digit numbers by class 3. Key concepts in addition include:
- Adding Single-Digit Numbers: Starting with adding numbers like 2 + 3 or 4 + 5.
- Using Visual Aids: Using objects, fingers, or pictures to help students visualize the addition process.
- Introduction to Carrying: By class 2, students begin to learn about carrying over when the sum exceeds 9.
- Word Problems: Applying addition in real-life scenarios through simple word problems.
Subtraction: Learning to Take Away
Subtraction is the process of taking one number away from another. It is closely related to addition and is often taught alongside it. For students in classes 1 to 3, subtraction involves:
- Subtracting Single-Digit Numbers: Simple problems like 7 – 4 or 9 – 3.
- Using Counters or Number Lines: Visual aids like counters or number lines help in understanding the concept of subtraction.
- Borrowing: In class 3, students learn about borrowing when subtracting larger numbers.
- Application in Word Problems: Like addition, subtraction is applied in various real-life scenarios through word problems.
Multiplication: An Introduction to Repeated Addition
Multiplication is essentially repeated addition. For example, 3 multiplied by 4 (3 x 4) is the same as adding 3 four times (3 + 3 + 3 + 3). The key concepts include:
- Learning Multiplication Tables: Starting with smaller tables (up to 5) in class 2 and moving up to 10 by class 3.
- Using Arrays: Visual representations like arrays or grids to show multiplication.
- Real-Life Applications: Simple word problems that involve counting groups of objects.
- Introduction to the Concept of Area: Understanding multiplication through the concept of area (length x width).
Division: Understanding Equal Sharing
Division is the process of splitting a number into equal parts. For students in classes 1 to 3, the focus is on understanding the basic concept and its relationship with multiplication.
- Division as Repeated Subtraction: Understanding division by repeatedly subtracting the divisor from the dividend.
- Simple Division Facts: Learning basic division facts related to multiplication tables.
- Using Visual Aids: Sharing objects equally among groups to represent division.
- Word Problems: Solving simple problems that involve dividing objects or quantities equally.
Understanding Place Value: The Basis for Larger Numbers
Place value is a fundamental concept in Basic Mathematics that helps students understand the value of digits in a number. For instance, in the number 345, the digit 5 is in the ‘ones’ place, 4 is in the ‘tens’ place, and 3 is in the ‘hundreds’ place. Key aspects include:
- Understanding Ones, Tens, and Hundreds: Learning the value of digits based on their position.
- Using Place Value Charts: Visual tools like charts or blocks to represent numbers.
- Expanding Numbers: Breaking down numbers into their place values (e.g., 345 = 300 + 40 + 5).
- Comparing and Ordering Numbers: Using place value to compare and order numbers from smallest to largest.
Simple Fractions: The Introduction to Parts of a Whole
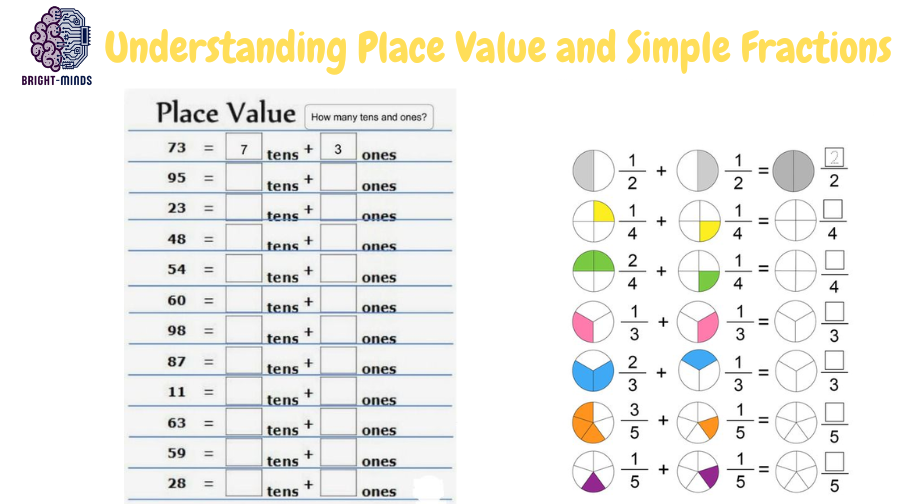
Fractions represent parts of a whole and are introduced in class 3. The basic concepts include:
- Understanding Halves and Quarters: Learning to divide objects or quantities into two or four equal parts.
- Visual Representation: Using pie charts, fraction bars, or everyday objects like pizzas to visualize fractions.
- Equivalent Fractions: Understanding that different fractions can represent the same quantity (e.g., 2/4 is the same as 1/2).
- Simple Addition of Fractions: Adding fractions with the same denominator (e.g., 1/4 + 1/4 = 2/4).
Engaging Math Games and Puzzles

Mathematics doesn’t have to be dull or intimidating. Engaging students with math games and puzzles can enhance their understanding and make learning fun.
- Number Matching Games: Matching numbers with their corresponding addition or subtraction problems.
- Multiplication Bingo: A fun way to reinforce multiplication tables.
- Fraction Puzzles: Using fraction tiles or pie charts to complete puzzles.
- Interactive Math Apps: Utilizing educational apps that offer interactive math challenges for kids.
Conclusion
The early years of a child’s education are critical for building a strong mathematical foundation. By mastering the Basic Mathematics concepts of addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, place value, and simple fractions, students in classes 1 to 3 can develop the skills needed for more advanced mathematical learning. Engaging math games and puzzles further enhance their understanding and make the learning process enjoyable.
you may be interested in this blog here:-
विद्यार्थ्यांकडून शिक्षकांना धन्यवाद संदेश – bright-minds ..
