Introduction
Language is like a large puzzle with many components. These components are known as
elements of speech, and each one has a specific purpose in assisting us in constructing
coherent sentences. You should study components of speech if you’ve ever pondered what
constitutes a complete sentence.
1. What Are Parts of Speech?
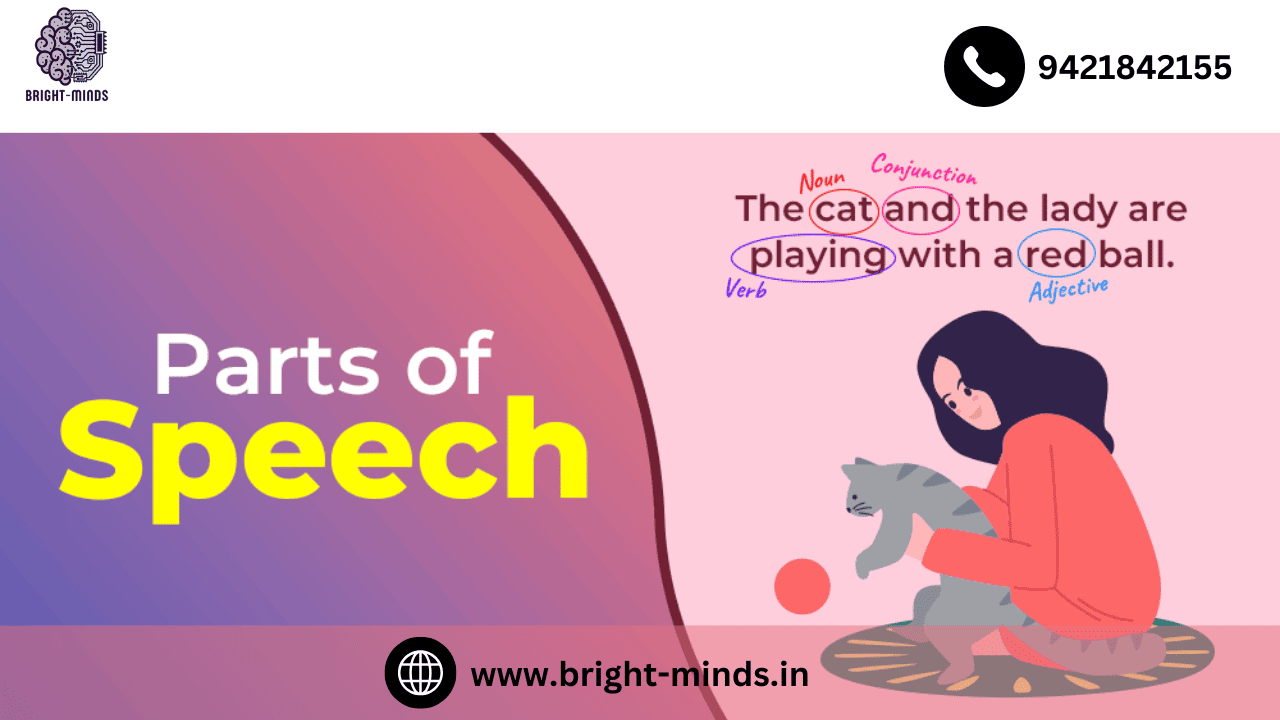
● Think of a sentence as a group of players cooperating. Although each participant has a
distinct function, they must all work together to complete the task. The components of
speech in a sentence are like the players, each of whom has a certain role to play. The
fundamental linguistic building blocks known as parts of speech aid in the organization of
our thoughts.
● Every child should be familiar with the following most common components of speech:
● Pronouns and Nouns
● Adjectives and Verbs
● Adverbs
● Prepositions
● Conjunctions
● Interjections
2. Nouns: The Name Game
Any term that names a person, location, object, or concept is a noun. Nouns are the people,
places, and things that the phrase is discussing; they are like the sentence’s stars. There
wouldn’t be much to discuss without nouns!
Noun Examples:
Person: dog, sister, or teacher
Location: beach, park, or school
Item: apple, pencil, and book
Concept: joy, love, and liberty
Example Sentence: The dog ran to the park, to put it simply.
Since “dog” and “park” name an object and a location, respectively, they are nouns in this
statemen
3. Pronouns: Replacing Nouns
A term that replaces a noun is called a pronoun. To make sentences sound more fluid and less
repetitive, we employ pronouns rather than repeatedly using the same term. Without explicitly
naming them, pronouns can be used to refer to persons, objects, or locations.
Examples of Pronouns:
● I, you, he, she, it, we, they
Example Sentence:
Sarah visited the shop. She purchased some candies.
To prevent duplication, the pronoun “she” takes the place of the noun “Sarah” in this phrase.
4. Verbs: Action and Being
Sarah visited the shop. She purchased some candies.
To prevent duplication, the pronoun “she” takes the place of the noun “Sarah” in this phrase.
Examples of Verbs:
● Action verbs: run, jump, swim, write
● State of being verbs: am, is, are, was, were
Example Sentence:
Tommy runs fast.
In this sentence, “runs” is the verb because it shows the action of Tommy.
5. Adjectives: Describing Words
A word that characterizes a noun is called an adjective. It is beneficial to include more
information about the noun, such as its appearance, texture, or number.
Examples of Adjectives:
● Big, small, tall, short
● Happy, sad, angry, excited
● Red, blue, green, yellow
Example Sentence:
The big, fluffy dog is sleeping.
In this sentence, “big” and “fluffy” are adjectives that describe the noun “dog.”
6. Adverbs: Describing Actions
Words that characterize verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs are called adverbs. It frequently
provides information on how, when, where, and to what extent something is done. By providing
more details about the action, adverbs can add interest to sentences.
Examples of Adverbs:
● How?: quickly, carefully, slowly
● When?: yesterday, soon, always
● Where?: here, there, everywhere
Example Sentence:
She ran quickly to the bus stop.
In this sentence, “quickly” is an adverb because it tells us how she ran.
7. Interjections: Expressing Emotions
A word that characterizes a noun is called an adjective. It is beneficial to include more
information about the noun, such as its appearance, texture, or number.
Examples of Interjections:
● Wow! Ouch! Hooray! Oh no! Yikes!
Example Sentence:
Wow! That was an amazing performance!
In this sentence, “Wow!” is an interjection because it expresses excitement.
8. Prepositions: Showing Relationships
A term that indicates the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the
sentence is called a preposition. It frequently provides us with direction, time, and position
information.
Examples of Prepositions:
● in, on, at, under, over, between, before, after, during
Example Sentence:
The cat is under the table.
In this sentence, “under” is the preposition because it shows the relationship between the cat
and the table.
9. Conjunctions: Joining Words
A word that joins words, phrases, or clauses is called a conjunction. Similar to a bridge, it
facilitates the integration of disparate sentence components.
Examples of Conjunctions:
● and, but, or, because, so, yet
Example Sentence:
I want to play soccer, but it’s raining.
In this sentence, “but” is the conjunction because it connects two ideas in the sentence.
Why Are Parts of Speech Important?
Learning about the elements of speech helps us understand how language works.
Understanding the purpose of each speech component may help us create stronger sentences
and communicate more successfully. It’s comparable to understanding a game’s rules in that
you can play it more skillfully after you understand how each element interacts.
Parts of speech also make writing more engaging. For example, you can use adjectives to give
a more thorough description or the right verb to illustrate a certain action. You can use different
parts of speech creatively to bring your work to life!
Fun Ways to Practice Parts of Speech
- It’s time to practice now that you are aware of the parts of speech! The following
enjoyable exercises will help you improve your ability to recognize sentence components
of speech: - Speech Components Organizing: Sort a list of words into the appropriate part of
speech by writing them down. Dog (noun), fast (adverb), play (verb), and joyful
(adjective) are a few examples. - Creating Sentences: Make careful to use a range of speech parts when you write your
own sentences. After that, go back and mark the speech components in your statement. - Speech Components Bingo: Make a bingo card with various speech components.
Check off the parts of speech you hear while watching a video or reading a tale.
Conclusion
Knowing the rules of a fun language game is similar to understanding the parts of speech. You
can begin creating your own sentences and clearly expressing your ideas once you understand
the fundamentals, which include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions,
conjunctions, and interjections.
Also Read:
https://bright-minds.in/unlocking-word-meaning-for-class-ukg-english-to-hindi/